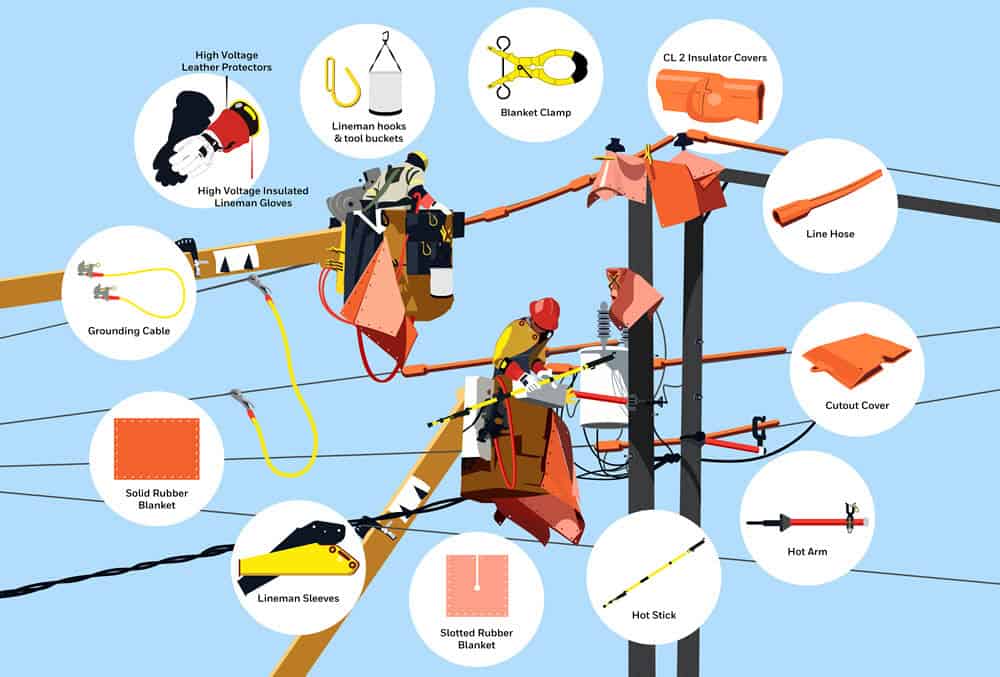
We’re excited to introduce our latest downloadable infographic showcasing the essential high voltage safety equipment utility line workers rely on every day. Whether you’re training new crew members or brushing up on the tools of the trade, this resource visually Read More
Author: Burlington Safety Laboratory
New Facility Focuses on High Voltage Grounding Sets, Cables, and Insulated Jumpers
UPDATED – April 23, 2025 It has been a lot of work and a long time coming, but we are thrilled to announce that production in our new facility in Westminster, CA is up and running! We organized the facility Read More
NEW – 2024 Electrical Safety Catalog
It’s here! Download your copy of the new 2024 Electrical Safety Catalog from Honeywell Salisbury now. Click to Download Electrical Safety Catalog (pdf) This catalog has it all including a brief history of Salisbury, Electrical Safety Gloves and Lineman’s Sleeves, Read More
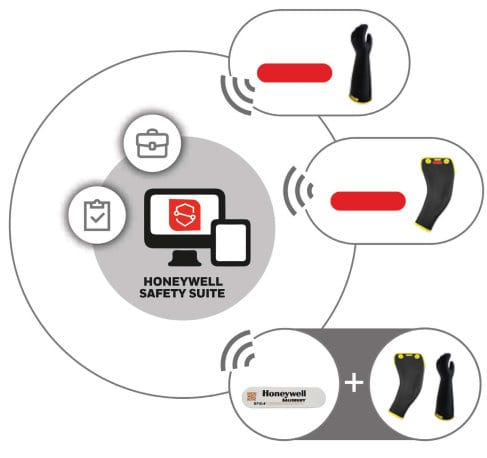
NEW – Lineman’s Rubber Gloves and Sleeves with RFID Capabilities
Burlington Safety Laboratory is excited to announce that we now offer RFID enabled rubber electrician’s safety gloves and sleeves as part of the growing line of RFID Safety Suite Equipment and Management Bundle from Honeywell – Salisbury. Bring new value Read More
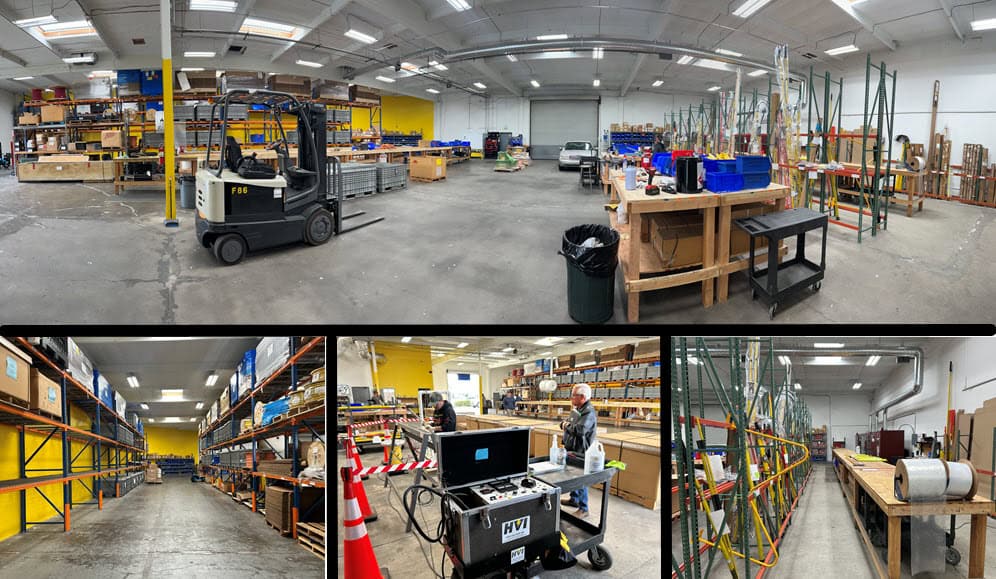
Facility Expansion for Enhanced Electrical Grounding Testing Capabilities
We are thrilled to share some exciting news from Burlington Safety Laboratory! As part of our ongoing commitment to excellence and safety in electrical testing, we have recently expanded into a new, state-of-the-art industrial facility. This move marks a significant Read More
Safety Day Event Recap
We would like to thank everyone who attended the Burlington Safety Laboratory Safety Day event we hosted at our Burlington, NJ facility on June 4th, 2024. Attendance at the event was even higher than expected and made for a great Read More
Join us for a Safety Day!
NOTE: This blog post references an event from the past (6/4/2024) Has your curiosity ever sparked about the process of electrical PPE testing? Here’s your chance to learn all about it and us! Explore the importance of electrical safety and Read More
Lab Testing of Rubber Gloves and Products
Rubber is a common material valued for its versatility and durability, but it can degrade over time. Factors that influence the integrity of rubber products include regular use, environmental changes, improper storage, exposure to sharp objects and dirt, and contact Read More
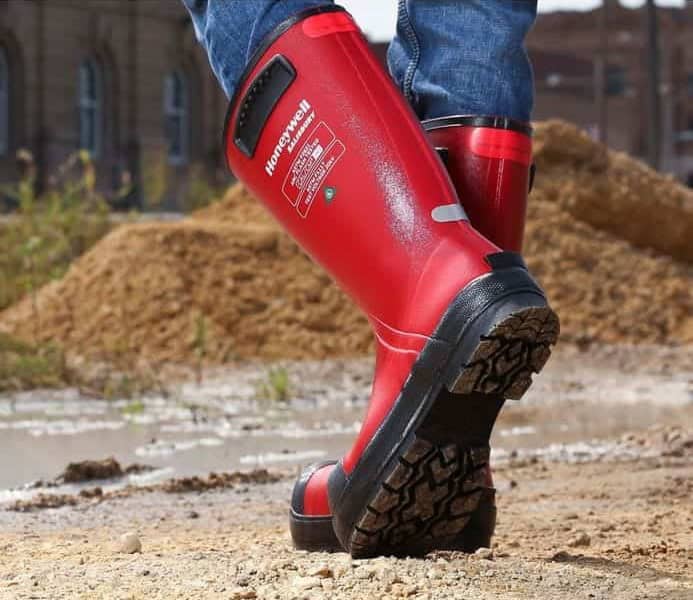
Dielectric Boots and Electrical Rubber Footwear Explained
A sturdy pair of dielectric rubber footwear is a critical component of electrical safety PPE, protecting workers in high-voltage environments. Utility workers, repair technicians, and employees working in high voltage environments can all benefit from the full-fledged protection of insulating Read More